On 27 September this blog was a victim of Google’s Panda update.
Google Panda is a change to the search results algorithm that aims to lower the rank of “low-quality sites”.
Over the years I have found a helpful motivation to writing blog posts is to keep an eye on my visitor statistics. Once the graph starts to dip towards the X axis it is time to put up another story. Handily WordPress produces a nice little graph showing daily activity on the website.
So you can imagine I was more than a little surprised when on 27 September I noticed my hit rate had reduced from 800 a day to 80. After a few days I could see the numbers were not going back up to their previous level and so started to investigate why.
I still don’t have a definitive answer from Google Webmaster site about what caused the drop. My guess is that they became aware of the TypePad copy of this blog.
The history of why I ended up with two versions are too long and boring to go into, but it relates to being an early adopter of blogging at the British Library.
I was aware this duplication could potentially be a problem for Google, who are always on the look-out for people ‘scamming’ their way up the rankings. However, after five years I had assumed they weren’t bothered by my two sites… It seems I was wrong.
A bit of research on the Google Webmasters forum found quite a few other bloggers complaining about plummeting traffic on their pages. And the explanation offered was that the regular Panda index update had demoted their site in the search results.
So all this is a rather long winded explanation as to why my TypePad blog posts now consist of just a short introduction followed by a link to this WordPress site.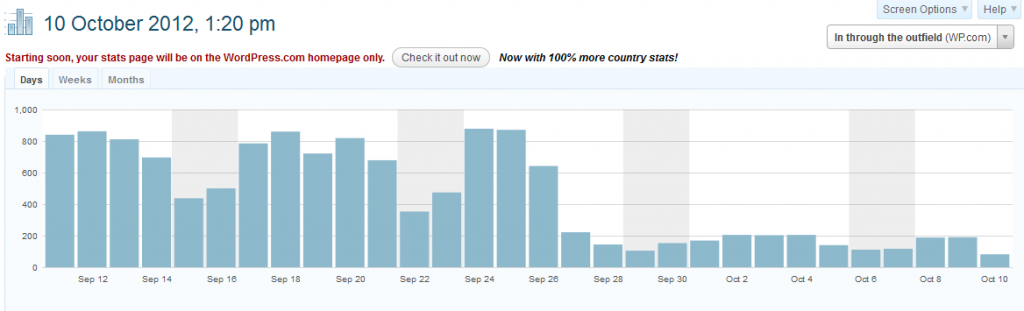
In case the same thing happens to your site. Here is the official advice from Google:
What counts as a high-quality site?
Our site quality algorithms are aimed at helping people find “high-quality” sites by reducing the rankings of low-quality content. The recent “Panda” change tackles the difficult task of algorithmically assessing website quality. Taking a step back, we wanted to explain some of the ideas and research that drive the development of our algorithms.
Below are some questions that one could use to assess the “quality” of a page or an article. These are the kinds of questions we ask ourselves as we write algorithms that attempt to assess site quality. Think of it as our take at encoding what we think our users want.
Of course, we aren’t disclosing the actual ranking signals used in our algorithms because we don’t want folks to game our search results; but if you want to step into Google’s mindset, the questions below provide some guidance on how we’ve been looking at the issue:
- Would you trust the information presented in this article?
- Is this article written by an expert or enthusiast who knows the topic well, or is it more shallow in nature?
- Does the site have duplicate, overlapping, or redundant articles on the same or similar topics with slightly different keyword variations?
- Would you be comfortable giving your credit card information to this site?
- Does this article have spelling, stylistic, or factual errors?
- Are the topics driven by genuine interests of readers of the site, or does the site generate content by attempting to guess what might rank well in search engines?
- Does the article provide original content or information, original reporting, original research, or original analysis?
- Does the page provide substantial value when compared to other pages in search results?
- How much quality control is done on content?
- Does the article describe both sides of a story?
- Is the site a recognized authority on its topic?
- Is the content mass-produced by or outsourced to a large number of creators, or spread across a large network of sites, so that individual pages or sites don’t get as much attention or care?
- Was the article edited well, or does it appear sloppy or hastily produced?
- For a health related query, would you trust information from this site?
- Would you recognize this site as an authoritative source when mentioned by name?
- Does this article provide a complete or comprehensive description of the topic?
- Does this article contain insightful analysis or interesting information that is beyond obvious?
- Is this the sort of page you’d want to bookmark, share with a friend, or recommend?
- Does this article have an excessive amount of ads that distract from or interfere with the main content?
- Would you expect to see this article in a printed magazine, encyclopedia or book?
- Are the articles short, unsubstantial, or otherwise lacking in helpful specifics?
- Are the pages produced with great care and attention to detail vs. less attention to detail?
- Would users complain when they see pages from this site?
Writing an algorithm to assess page or site quality is a much harder task, but we hope the questions above give some insight into how we try to write algorithms that distinguish higher-quality sites from lower-quality sites.


